



RLX COMPONENTS s.r.o. , Electronic Components Distributor.
RLX COMPONENTS s.r.o. , Electronic Components Distributor.
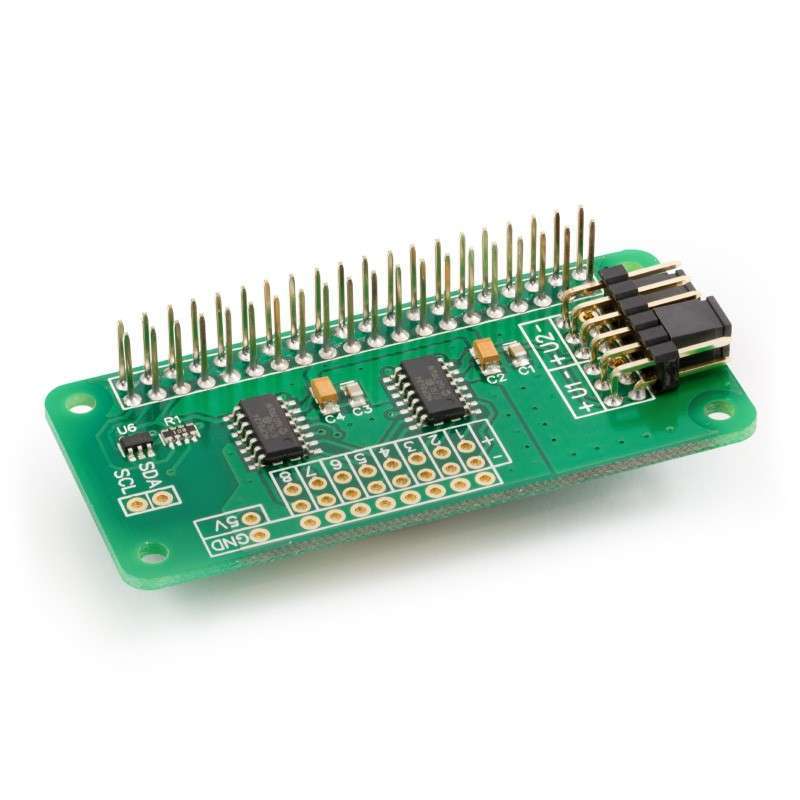
ADC Differential Pi (AB Electronics UK) 8 x 18-bit differential inputs, 4 ADC Differential Pi boards on a single Raspberry Pi
The ADC Differential Pi is an 8 channel 18 bit analogue to digital converter designed to work with the Raspberry Pi. The ADC Differential Pi is based on two Microchip MCP3424 A/D converters each containing 4 analogue inputs. The MCP3424 is a delta-sigma A/D converter with low noise differential inputs.
Not sure which ADC you need ? Check our Analogue to Digital Buyers guide to compare our ADC expansion boards.
We designed the ADC Differential Pi as a companion for our ADC Pi Plus and ADC Pi Zero. Unlike the ADC Pi Plus the ADC Differential Pi does not include any voltage dividers so the inputs can be used to measure a differential voltage range of ±2.048V. This is useful for measuring inputs below ±2.048V or allows you to use your own voltage divider to measure higher voltages.
The ADC Differential Pi is powered through the host Raspberry Pi using the GPIO port and extended pins on the GPIO connector allow you to stack the ADC Differential Pi along with other expansion boards.
The two MCP3424 A/D converters communicate via i2c to the host Raspberry Pi giving you eight analogue inputs to use. A logic level converter is included on the ADC Pi Plus board giving you a buffered 5V i2c port making it easy to add other I2C devices which operate at 5 volts without damaging the raspberry pi 3.3 volt i2c port. The i2c buffer uses N-channel mosfets with a maximum drain current of 100mA.
The I2C address bits are selectable using the on-board jumpers. The MCP3424 supports up to 8 different I2C addresses so with two A/D converters on each ADC Differential Pi you can stack up to 4 ADC Differential Pi boards on a single Raspberry Pi giving you 32 ADC inputs.
The MCP3424 contains an on-board 2.048V reference voltage with an input range of ±2.048V differentially (full scale range of 4.096V/PGA). A programmable Gain Amplifier gives the user a selectable gain of x1, x2, x4 or x8 before the analogue to digital conversion takes place.
The data rate for analogue to digital conversions is 3.75 (18 bit), 15 (16 bit), 60 (14 bit) or 240 (12 bit) samples per second. Data rate and resolution can be configured within software using the I2C interface.
We have a knowledge base article, ADC Sample Rate Comparisonwhich has more detailed sample information and test scripts to compare the different MCP2424 ADC chip bit and sample rates.
Unused inputs should be tied to ground.
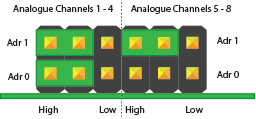
The MCP3424 analogue to digital converter contains two address select pins which can be tied to Vss, Vdd or left floating. This gives 8 possible I2C addresses for each chip. The ADC Differential Pi contains two MCP3424 chips so you can stack up to 4 ADC Differential Pi boards on a single Raspberry Pi. To simplify address selection on the ADC Differential Pi we have included a set of address selection pins which can be configured using the included jumpers. The illustrations below show the four recommended configurations for your ADC Differential Pi and the associated I2C addresses.
Note:
Disconnect the ADC Differential Pi from the Raspberry Pi before changing the address pins. You may need to short the 5V and ground with a resistor to discharge the capacitors in order for the new addresses to be recognised.
| Adr 0 | Adr 1 | I2C Address |
|---|---|---|
| Low or Float | Low or Float | 0x68 |
| Low | Float | 0x69 |
| Low | High | 0x6A |
| Float | Low | 0x6B |
| High | Low | 0x6C |
| High | Float | 0x6D |
| High | High | 0x6E |
| Float | High | 0x6F |
Do not under any circumstanced connect the two centre pins together. This will create a direct short between the 5V and ground pins and will damage or destroy your Raspberry Pi and ADC Pi Plus board.

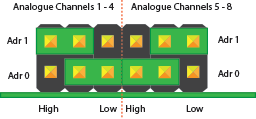
Configuration 1:
Analogue Channels 1-4 = I2C Address: 0x68
Analogue Channels 5-8 = I2C Address: 0x69
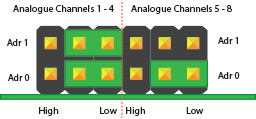
Configuration 2:
Analogue Channels 1-4 = I2C Address: 0x6A
Analogue Channels 5-8 = I2C Address: 0x6B
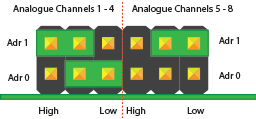
Configuration 3:
Analogue Channels 1-4 = I2C Address: 0x6C
Analogue Channels 5-8 = I2C Address: 0x6D
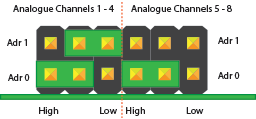
Configuration 4:
Analogue Channels 1-4 = I2C Address: 0x6E
Analogue Channels 5-8 = I2C Address: 0x6F
| Model | Status |
|---|---|
| Raspberry Pi Model A | No |
| Raspberry Pi Model B | No |
| Raspberry Pi 1 Model A+ | Yes |
| Raspberry Pi 1 Model B+ | Yes |
| Raspberry Pi 2 Model B | Yes |
| Raspberry Pi 3 Model B | Yes |
| Raspberry Pi Zero | Yes |
| Raspberry Pi Zero W | Yes |
| ODroid C1 | Yes |
| ODroid C2 | Yes |
| Orange Pi | Yes |
| Asus Tinker Board | Yes |
| Spec | Ratings |
|---|---|
| Vdd (5V pin on I2C bus) | 5.0V |
| All AD inputs and outputs | VSS–0.4V to VDD+0.4 V |
| Current at Input Pins | ±2 mA |
| I2C SDA/SCL voltage | 5.0 V |
| I2C port current | 100 mA |
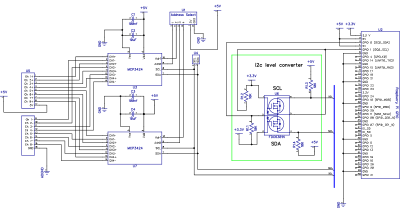
Click to download schematic PDF.
The ADC Differential Pi is supplied with the 40 pin GPIO connector and the 12 pin address connector unsoldered.
Before using the ADC Differential Pi you will need to solder both connectors onto the PCB. We suggest soldering the 40 pin GPIO connector first and then the address select connector. Soldering the address select connector first will make it difficult to access the three corner pins on the GPIO connector.
Assembly for the ADC Differential Pi is the same as on our ADC Pi Plus. Watch the assembly video, best viewed in 1080p high quality mode:
Download and print our PCB Header Assembly Jig to hold your circuit board when soldering the header pins.
Click image to enlarge
We have Python, Arduino, C, C++, Node.js and Windows 10 IOT libraries available for this expansion board. You can download all of the libraries from github at:
https://github.com/abelectronicsuk/ or click on the logos below for your selected programming language